The Oral Biome: A Surprising Gateway to Gut and Brain Health
Dr. Karen Plymel, Functional Medicine Expert
When you think about gut health, you probably picture probiotics, digestion, or feeling bloated but there is an important piece of the puzzle we often miss—the oral microbiome.
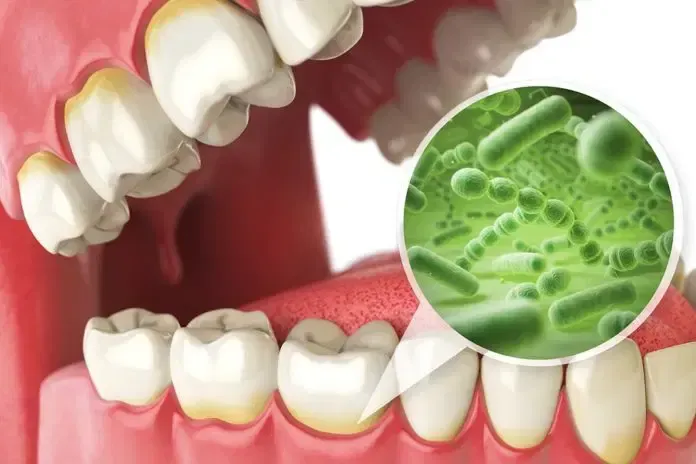
Your mouth is more than just the start of the digestive tract. It is home to a complex community of over 700 species of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and other microbes. This ecosystem, known as the oral microbiome, plays a crucial role in not only dental health but also the health of the gut and even the brain.
Let’s take a closer look at how the oral biome connects with the gut microbiome—and how both influence your brain health.
The Oral-Gut Connection: Microbes on the Move
Every time you swallow, you send thousands of microbes from your mouth down into your gut. When the oral microbiome functions properly, it allows helpful bacteria to aid your gut microbiome. However, when the oral cavity undergoes an imbalance, also called oral dysbiosis, opportunistic pathogens like Fusobacterium nucleatum and Porphyromonas gingivalis can enter the gastrointestinal tract and wreak havoc. Studies have shown that these oral pathogens can:
- Disrupt the gut’s microbial balance
- Increased inflammatory responses both in the gut and systemically
- Compromise gut barrier integrity (leading to "leaky gut")
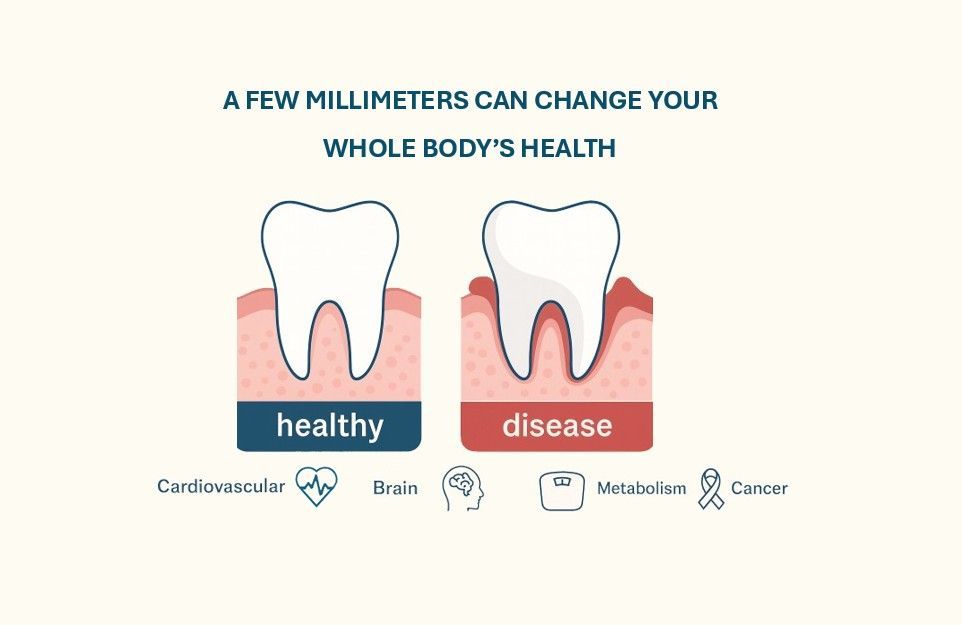
The shift in microbiome location helps to understand the association between poor oral hygiene and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and even metabolic syndromes.
Oral Microbiome and Brain Health: The Inflammation Route
Taking care of your oral hygiene goes beyond preventing cavities; it is important for your brain health.
There is emerging evidence associating chronic gum disease with cognitive conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and general cognitive decline. This association occurs when harmful bacteria from the mouth:
- Penetrate the systemic circulation through inflamed or bleeding gums
- Enter the brain and bypass the blood-brain barrier
- Induce neuroinflammation and likely aid in the development of amyloid plaques
One major culprit is Porphyromonas gingivalis, as its pathogenic strains have shown to secrete toxins (gingipains) within the brains of Alzheimer's patients, further showcasing the extent in which the oral microbiome can affect the body.
The Oral Gut-Brain Axis: A 3-Way Communication System
The oral-gut-brain axis is the interactions that occur between your mouth and digestive system with the brain. The gut-brain axis has been highly regarded and widely studied; however, science is now showing that your oral health may play a role in influencing this relationship to some degree.
A balanced oral microbiome contributes to:
- Appropriate digestion and nutrient intake.
- Mood stabilization and mental acuity triggered by microbial byproducts like short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
- Lower levels of inflammation throughout the body can help reduce the risk of anxiety, brain fog, and depression."
The onset of oral dysbiosis can also lead to gut dysbiosis, weakening both the gut and brain barriers. This can increase chronic inflammation, which may contribute to physical and mental symptoms that affect overall well-being.
Tips to Support a Healthy Oral Microbiome
As with the gut, the mouth requires certain practices to thrive. Here’s how to nurture the oral microbiome:
- Avoid harsh mouthwashes: Alcohol-based rinses may kill beneficial bacteria.
- Brush and floss regularly: But don’t overdo it—gentle cleaning prevents inflammation.
- Eat a diverse, whole-foods diet: Fiber and polyphenols (like those in green tea and berries) support beneficial bacteria.
- Stay hydrated: Saliva helps regulate pH and microbial balance.
- Consider oral probiotics: Especially strains like Streptococcus salivarius K12 and M18.
Also, chronic mouth breathing, high sugar intake, and nutrient deficiencies (especially vitamin D and K2) can shift the oral microbiome toward dysbiosis.
The Takeaway
Your mouth is one of the body’s first lines of defense when it comes to protecting your gut and brain. Good oral health isn’t just about your teeth, it reflects the health of your entire body. By supporting the delicate microbial balance in your mouth, you can help build a stronger foundation for gut health and cognitive resilience.